
Addressing Nitrogen Deficiency in Organic Crop Production
In the last few articles that we have recently been publishing, a key issue has over and over crept up. This is the issue of the challenges that organic crop production faces. These challenges as outlined by a recent study were found to be the lack of nitrogen as a nutrient and the other one was seen as the lack of proper mechanism towards tackling pests and weeds. Organic food production shies away from the use of synthetic chemicals and fertilizers. Nitrogen is one of the nutrients needed in large amounts by crops and its deficiency results in decreased productivity.
Towards researching on how best nitrogen deficiency can be addressed issue, we would like to explore issues surrounding nitrogen as a nutrient and ways that organic food production can achieve this nutrient. As these articles have illustrated, it can be concluded that nitrogen is a big challenge to be addressed in organic crop growth. There exists a gap in the nitrogen-supply triggered by cover crops and compost manure and nitrogen demand by crops that are being grown using organic methods.
Nitrogen is found in the soil in various forms either as a gas in spaces within the soil or in the forms of organic or organic nitrogen. However, the forms that are ready for absorption by the plant are the ammonium and the nitrate. Nitrogen is needed by several plant processes and blocks such as the DNA. It’s also a part of amino acid vital for facilitating plant growth. Photosynthesis is believed to be optimized in a plant with ample nitrogen.
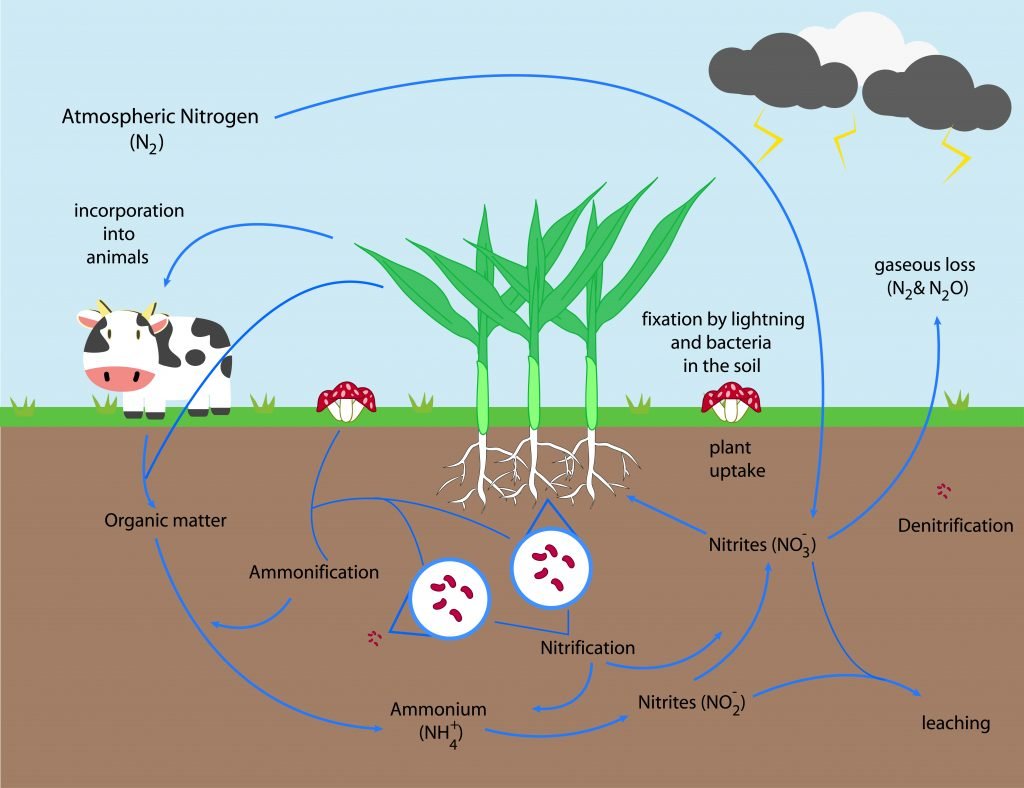
The Nitrogen Cycle
Nitrogen absorbed by the plants is in the form of nitrated. This nitrate can also be lost to the atmosphere by de-nitrification process. Plants are then consumed by animals that in turn produce organic matter. Other fixation processes also add nitrogen into the soil from the atmosphere and these includes lighting fixation and bacteria fixation. Fixation is a process which converts the nitrogen gas in the atmosphere to a molecule that can be absorbed by plants. This organic matter is further processed in the soil by mineralization converting it into ammonium. Two processes of nitrification on the ammonium result in the formation of nitrites and nitrates respectively. Nitrification is an oxidation process whereby oxygen molecule is added. Nitrites can be lost or leaked into water bodies through the process of leaching. This cycle of nitrogen addition and loss forms what’s known as the nitrogen cycle. Nitrogen is normally lost from the soil as earlier pointed out through de-nitrification, leaching, run-off and by plant absorption. Further, volatization does also lead to loss.
Sources of Nitrogen for organic crop production
What are the available nitrogen sources that organic farmers can use? Compositing is one of the best sources of nitrogen available. Though, the slow decomposition of the compost result in slow release of nitrogen into the soil making it not effective in meeting the crop needs. This decomposition takes several months and in some instance takes years to fully release the nitrogen. The selection of materials in making the compost is a factor to consider. Materials with low carbon to nitrogen cycle are ideal and include animal wastes, hay and weeds. These tend to rapidly decompose availing the nitrogen to the crops faster. Other factors to enhance the making of an ideal compost includes; proper aeration to enable adequate micro-organisms activity, maintaining an ideal temperature, moisture, the size of the materials and the volume of the compost.
AT this juncture, we need to point out that there exist a difference between manure and compost. Manure is the fresh excretion from the animal waste while the compositing entails the subjection of the manure to ideal conditions that allow proper decomposition of manure to make compost. A huge chunk of nitrogen in the manure is quite unstable and is in the form of ammonia which is subject to volatization and can’t be used by crops in this form while a small fraction of the nitrogen content can be directly used by the plant.
The other method of enhancing sufficient nitrogen supply in organic farming is the use of cover crops. Cover crops have been shown to cause biological nitrogen fixation in addition to decreasing soil erosion, leaching of nitrate and formation of organic matter that can further provide nutrients to other crops. Cover crops are considered to be legumes and grass. Legumes include beans, peas, soybeans, lentils among others. They are generally seen as vegetables or grass and are believed to have roots capable of encouraging rhizobia bacteria responsible for fixing nitrogen from nitrite to make it nitrate that can be absorbed by the plant.
The use of commercial organic fertilizers is another way by which nitrogen can be added to crops fields. There are several commercial organic fertilizers specifically manufactured to cater for different crop species. They are either plant or animal based. There is also sodium nitrate that is mined however; in some countries it has been limited on the extent of its use.













Too much leafy compost just makes greens bolt. A good crop of lupins or other nitrogen fixer. Clover.
Bees love clover and I love clover honey….win win.
What is “too much”
Creci Elens I think just more leaves than anything else in your compost. I am no expert at all, this was my experience. When i asked my gardener friend why my greens bolted, he suggested too much leaf litter in my compost. i had many Sycamore leaves from a big tree in the back yard.
Antoinette Stones Balance
Antoinette Stones
I would avoid Sycamore leaves as they contain a natural herbicide to suppress weed and grass competition.
I’m surprised the article doesn’t mention the use of legume trees, only legume cover crops. Tree legumes are an essential component of both food forest system and alley cropping systems. For example in South America the Inga edulis has been used very successfully in alley cropping systems with, organic vegetables grown between the rows of lopped trees. In this situation the cut branches and leaves are used as a mulch layer instead of growing a cover crop. The Inga fixes atmospheric nitrogen into the soil via nodules on its roots and from the decomposing leaves. The Inga leaves in conjunction with soil mycorrhiza also recycles phosphate, which is often the limiting factor in tropical soils.
Nitro’d up citrus tree yesterday!!
ADD LOTS OF MULCH !
I find this article very informative! My uncle is researching organic crop production so I’m kinda interested in it as well. Because of nitrogen deficiency, there’s a decreased productivity. However, this article stressed that there are plant and animal-based organic fertilizers which can actually add nitrogen to the crops. Thanks for this information!