Finding Ways to Prevent Water Waste and Save on Rising Produce Costs During California’s Historic Drought
THE CURRENT STATE OF CALIFORNIA’S UNPRECEDENTED DROUGHT
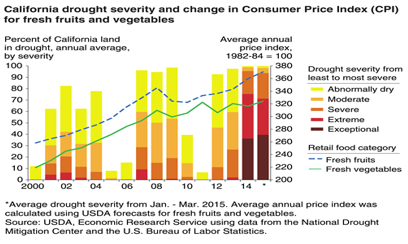
Startling Statistics
California is currently in its fourth year of a severe drought. The United States Drought Monitor estimates that over 90 percent of California is currently experiencing “severe” to “exceptional” drought conditions. For farmers, the increasing scarcity of water has been devastating. According to the American Farmland Trust, California is home to 27 million acres of cropland. Nine million of those acres are irrigated farmlands, requiring a steady water supply. Crops typically requiring regular irrigation include vegetables (1.1 million acres), orchards and vineyards (3.1 million acres), and forage crops (1.7 million acres). Roughly 7 out of 10 irrigated farms in California depend entirely, or at least in part, on surface water allocated from state and federal projects. In 2014, farmers received zero water allocations from federal projects and only one-fifth of the water that they would normally receive from state water projects.
The shortage of water for agriculture has forced many farmers to fallow thousands of acres of their land in order to allocate what little water they receive to producing a successful harvest. Some reports estimate that in 2014 alone nearly half a million acres of California farmland were fallowed as a result of the water shortage. Other farmers have chosen to switch their crops to more drought-friendly varieties, including GMO seed varieties designed to thrive in soil with lower moisture content.
The Governor and Local Communities Take Action
Farmers have found some relief from favorable economic circumstances. For example, decreasing fuel prices and a surge in American imports have provided temporary relief from the crippling impact of the drought. In many communities, residents have started sourcing their food from local farmers and agricultural producers in an attempt to keep their businesses going through these tough economic times. Some local grocers are making an effort to source as much of their produce as they can from local farms as opposed to importing fruits and vegetables from other regions.
The State of California has taken action to help soften the blow of a fourth year of severe drought. On April 1, 2015, California Governor Jerry Brown signed an Executive Order mandating water restrictions for all California residents. This is the first time in California’s history that a mandatory water restriction has been set into place to combat drought-related issues. As part of the mandatory water cuts, residents will be required to reduce their water consumption by 25 percent, or face daily monetary fines. The executive order exempts farmers from the new requirement, noting just how badly many farmers have already been impacted.
INCREASES IN FRUIT AND VEGETABLE PRICES
California: The Horn of Plenty
To truly comprehend the impact that California’s drought may have on food prices, it is important to have an understanding of just how crucial California’s agricultural industry is to the nation and the world at large. Many people refer to California as the nation’s breadbasket. The rich soil and ideal weather conditions make it some of the most fertile planting soil in the world. It is no surprise, therefore, that California produces 400 different types of agricultural commodities and provides roughly half of the nation’s fruits, vegetables, and nuts.
California is the nation’s leading producer of many food staples, including avocados, broccoli, tomatoes, spinach, grapes, tree nuts, and dairy. According to a study conducted by the University of California Agricultural Issues Center, in 2013 California exported $4.16 billion worth of almonds and over $2.4 billion in dairy products. Other key California exports include wine, tree nuts, grapes, rice, cotton, and beef. Overall, the California Department of Food and Agriculture reports that California’s 77,900 farms earned over $46 billion for agricultural exports in 2013.
Produce Prices are Predicted to Increase as a Result of the Drought
The extent to which California’s drought will have an impact on produce prices depends on the overall severity of the drought and how the drought affects total crop yields. When it comes to produce, the most critical concern during a drought is the diminishing groundwater supply, which is typically needed to provide consistent irrigation to fruit and vegetable crops. In response to a groundwater supply shortage, many farmers choose to plant a smaller amount of a particular crop, or to plant an entirely different crop that is more tolerant to drought conditions.
According to the United States Department of Agriculture, when it comes to fruits and vegetables, any production impacts that may lead to price increases typically manifest at the supermarket shelves within one month. Produce is highly perishable, meaning that farmers cannot hold onto their produce until market prices are more favorable and consumers are more willing to buy. Other factors affecting the price of produce are labor wages, competitive imports, and fuel prices.
As a consequence of the growing scarcity of water for agriculture, the prices of fruits, vegetables, and other food products are expected to increase. For many farmers, the increasing cost of water and fallowing of fields requires them to raise the prices of the their crop yields.
How much of a price hike should consumers anticipate paying? According to the United States Department of Agriculture’s (USDA) reports, “[i]ncreases in retail prices for fresh fruits and vegetables in 2014 were primarily driven by an increase in the prices for citrus fruit.” Additionally, “[p]rices for fresh vegetables fell in 2014 after seeing higher than average price increases in 2013.”
These price increases will likely increase into 2015. USDA estimates that during 2015 supermarket prices will increase an additional 2 to 3 percent over 2014 prices. In particular, fresh fruit prices should rise between “2.5 to 3.5 percent and fresh vegetable prices 2.0 to 3.0 percent.” The USDA cautions, however, that California’s status as a crucial food producer gives it “the potential to drive prices for fruit, vegetables, dairy, and eggs up even further.” Ultimately, the USDA predicts that produce prices will continue to rise.
Other researchers have echoed the USDA’s conclusions regarding the escalating prices of produce as a result of California’s historic drought. For example, a study conducted by Timothy Richards at the W.P. Carey School of Business at Arizona State University predicts that the California drought could increase avocado prices up to 28 percent. According to the USDA, California produces 88 percent of avocadoes consumed throughout the United States. The study also concluded that the price of lettuce could increase between 62 cents and $2.44.
Richards believes that the most significant produce increases will occur with “avocadoes, berries, broccoli, grapes, lettuce, melons, peppers, tomatoes, and packaged salads.” Additionally, the California Farm Bureau has “projected that the average American family will spend about $500 more on food this year because of the drought.”
Of course, estimations regarding potential food price increases are not evaluated in a vacuum. Many other current events and factors play a part in determining whether consumers will pay more or less for fresh produce in the coming months. For example, the California Avocado Commission reports that part of the reason for the increased price of avocados, which rose 16 percent between 2013 and 2014, is the alternate bearing cycle of avocado trees. One year, the tree will produce a high volume of fruits, while producing substantially fewer fruits the following year. In 2013, California’s avocado yield was estimated at 500 million pounds. In 2014, total crop yield was projected at 350 million pounds.
Bridging the Gap with Imports from Abroad
Because California produces “nearly half of US-grown fruits, nuts and vegetables,” finding sources from out of state to supplement the drought’s impact on capacity is difficult. If the price of meat becomes high, grocers can turn to other sources of protein, like eggs and fish, to meet consumers’ needs. When it comes to fruits and vegetables, however, there are no comparable replacements to meet consumers’ demand for freshly grown food.
Since foreign countries that rely on California agriculture to meet their produce needs, like Canada, have started locating potential backup suppliers. Argentina, South Africa, and Australia offer bustling agricultural economies that may help foreign food importers bridge the gap caused by California’s drought. One impediment to sourcing produce from these other countries, however, is the tendency of certain produce, like lettuce and fruit, to perish during the journey. For example, citrus fruits and potatoes can be stored on a transatlantic cargo ship for over a week. Berries, fruits, and lettuces, however, must be kept at low temperatures and consumed within seven days.
Despite the logistical hurdles that must be overcome when importing produce from far away localities, some predict that California food wholesalers, distributers, and grocers will have no choice but to import food from Mexico, Central America, and South America. Current reports indicate that a number of fruits, like peaches, are being imported from Chile and are taking up a substantial share of California’s fruit market. According to the United States Trade Representative, Chile was the eighth largest source of agricultural imports for the United States in 2013, providing fish, seafood, and $1.8 billion in edible fruits and nuts. Mexico is the second largest supplier of agricultural imports for the United States, providing $17.7 billion worth of fresh vegetables, fruit, wine and beer, and snack foods. Canada is the largest source of agricultural imports for the United States, totaling $21.8 billion.
STRATEGIES TO MITIGATE WATER LOSS
Despite the enormity of California’s drought crisis there are many solutions and methodologies that can be used to help reduce water consumption and to reduce the cost of each trip to the grocery store for fruit and vegetables.
A New Water Paradigm Through Permaculture
At a more global level, a potential method for ensuring the optimization of water usage is Permaculture, which integrates resources, people, land and the environment through beneficial synergies. Permaculture enables farmers, urban agriculturalists, and rooftop gardeners to imitate the “no waste, closed loop systems” often observed in diverse natural ecosystems. Permaculture utilizes holistic approaches to restoring balance in ecosystems and ensuring that environmental assets, like land, water, and air, are revitalized, recharged, and protected.
When it comes to water management, the development and implementation of a water management system is an necessity. According to Geoff Lawton, it is about “gravity irrigation systems, water harvesting swales and simple systems”, when talking about the Permaculture Research Institute’s site going through his shires largest drought in a hundred years. Geoff continues on to explain that “even though the local village was cut off from water and water was issued in the street, we were able to continue to irrigate all kinds of crops, because we had an oversupply of water”.
Simple Ways to Save Water Around the House
One method that can be used to combat the current paradigm’s incredible water waste is a composting toilet. Composting toilets require little-to-no water, which enables users to cut their water bills drastically. A “dry composting converts human fecal material into a soil-like humus, which is essentially odorless and is scarcely 10 percent of the original volume.” Dry composting facilities are typically emptied once a year, depending on size, making them a low-maintenance way to fight water waste right in your home.
Many features of our modern water paradigm are designed to perform one-time usages of water. For example, “water enters a city, becomes contaminated with human and industrial wastes, and leaves the city dangerously polluted.” Current water systems allocate substantial amounts of water to the clearing away of human waste, typically into a sewer system. The results of this practice are devastating, and include disease, disruption of nutrient cycles, river death, and the formation of so-called “dead zones” in certain coastal areas.
Many regions have implemented water treatment facilities designed to make use of wastewater instead of dumping into lakes, rivers, or oceans. In California, Orange County constructed a $481 million treatment plant that converts sewage into water that is used to replenish local ground aquifers. As the California drought continues to affect farmers and other water users, the “flush and forget” system may become less common.
Other ways to save water around the home include installing water-efficient showerheads, toilets, laundry machines, and dishwashers. In some localities, newly installed appliances must comply with water efficiency requirements. If you cannot afford a low-flow toilet, simply place one to two inches of pebbles inside the bottom of your water tank, or fill two empty plastic bottles with rocks to weight hem down. This strategy alone can save over ten gallons of water each day. Additionally, do not let the water run while you clean produce. Fill the sink or a pan with clean water instead.
Permaculture at Home
Until legislators and policymakers adopt policies that encompass the full spectrum of water sources, individuals should consider implementing permaculture practices right in their backyards, rooftops, and homes. At its heart, permaculture is a design science that can be applied to any human habitat no matter how small the space may be.
According to Lawton, city environments are especially in need of the benefits that permaculture has to offer. A city block requires a remarkable amount of power and electricity to feed the many businesses, homes, and utilities that cover its acreage. One of the greatest features of permaculture is that it can be implemented in almost any setting or environments. There are ways to integrate permaculture practices even for folks who live in apartments, high-rises, or multi-tiered condos. For example, if you live in an apartment that features a balcony, consider growing sprouts or mushrooms.
When it comes to reducing water waste in cities, permaculture provides a method for ensuring that surplus water is returned to the environment or redirected to another source that can make good use of the water. For example, some cities have implemented permaculture streets, which feature controlled water runoff from hard surfaces towards gardens and other growing plants in need of hydration. Because cities are often burgeoning centers of design and intricate landscapes, they provide the perfect habitat for implementing creative permaculture strategies.
For homeowners, front and rear lawns represent ideal opportunities for implementing and experimenting with permaculture methodologies. In many cases, the amount of chemicals and treatments applied to lawns surpasses agricultural activities. Homeowners should consider converting up to half of their lawns to gardens or back to natural habitat. One of the greatest benefits of planting a home garden is the readily available bounty of fruits and vegetables that it provides. As Californians and produce consumers around the world begin to feel the drought’s impact on the price of fruits and vegetables, low-cost, home-based solutions may provide a solution. Permaculture offers an easy, efficient, and affordable way to grow produce right at home.
To achieve ultimate synergy, permaculture focuses on the habits and practices that characterize wild habitats like forests and pastures and mimics them in a controlled environment. Forests typically feature many different layers of vegetation growing side by side, including shrubs, plants, and trees. Among these vegetation layers are insects and animals. Each of these strands operate synergistically with one another as an ecosystem. In permaculture, the integrated relationship between all of these living things is known as a guild. While traditional gardening practices teach individuals how to plant gardens, permaculture focuses on equipping individuals to create and maintain successful guilds right at home. Ultimately, permaculture is a theory of design. Permaculture guilds typically have seven key components: (1) food for humans; (2) food for the soil; (3) diggers and miners; (4) groundcover; (5) climbers; (6) supporters; and (7) protectors. Each of these components work together to create a thriving synergistic system.
Many water saving strategies can be adopted for both permaculture gardens and traditional gardens. First, only water a lawn when it needs watering. To see if your lawn is in need of moisture, step on the grass. If the grass springs back up, it does not need water. If it lays flat, the lawn could use a little water. Intermittent deep-soakings are more effective at providing moisture to parched soil instead of frequent light showers. Also, the time of day that you choose to water can have an impact on how much of that moisture reaches the garden or lawn’s roots. Try to water during the night or early morning, and avoid watering when the sun is out or when it is windy. Adding a thick layer of mulch near the base of plants and tress can help retain moisture as it saturates through the soil. Mulch is particularly helpful for gardens that rely on drip systems. Composting is another helpful tool that can increase water retention. It also provides a dose of minerals and nutrients to the soil and vegetation. Many gardeners are surprised to learn that adding just one pound of compost material can yield “40 pounds of water retention.” Also, rain barrels can provide quick and easy surpluses of fresh water during the rainy season, and add aesthetic character to your lawn or garden.















I urge everyone who is interested in this article especially pertaining to the beinning regarding the 4 year drought to watch the documentary ‘what in the world are they spraying’. I know by observable evidence that droughts can now be man made, the question is whether deliberate or by accident? It does work quite convenientl for some corporaions agendas and has the potential to increase their income and control over various resources such as land, water as well as seed supply to name a few obvious ones. Please look into it
I’ve just had a look at “What in the world are they spraying”, which wasn’t what I thought it was going to be. I though it was about chemical pestacides/herbicides etc. Instead it was about chemtrails. I didn’t really know much about chemtrails, but having heard of them I stuck with the film, and I’m glad I did.
The film talks about unaccountable pH changes in soils, loss of soil microbial activity, the dying off of trees, extremely high levels of aluminum and barium in soil, and Monsanto’s new patent for an aluminum resistant gene to enable plants to grow in high aluminum soils. It interviews ecologists, soil scientists, chemists etc. and I think constructs a very interesting picture.
Hi,
“In many communities, residents have started sourcing their food from local farmers and agricultural producers in an attempt to keep their businesses going through these tough economic times. Some local grocers are making an effort to source as much of their produce as they can from local farms as opposed to importing fruits and vegetables from other regions.”
is it possible to get more food from local sources in times of a drought?
The actions farmers and private homeowners are taking make the drought situation worse:
Every square meter whose evaporation capabilitys are stopped (by not irrigating the lawn or letting a field rest) is adding to rising temperatures: Evaporation is dampening the effect of strong solar radiation which otherwise is converting barren landscapes into huge ovens.
The same goes with the cutting of withered trees: Strong hot winds (e.g. Santa-Ana winds) are like huge hair-dryers. Trees are acting like wind brakes therefore reducing evaporation and the loss of water (and humus). Even withered trees are braking the wind and can spend shade and reduce thereby the temperature of the soil.
The dry up of Owens Lake in November 2014 (70 km² were shallow flooded) will have a significant effect on nearby air temperatures in summer.
Can you recommend a speaker who can clearly state the reality of the drought situation and share innovative or overlooked ways for home gardeners to save water while growing veggies and ornamentals? I am in charge of public education for a 500 member organic community garden in West Los Angeles that presents workshops to the public and our members.
Hi Melody,
Warren Bush of https://www.quailsprings.org/warren/ is very well regarded.
Regards – Web Team
It’s so crazy how bad the drough is yet I have been driving around california for the last month and have seen so many bad farming methods! Like watering in the middle of the day when it’s 32degrees Celsius. It really seems so od some of the places america decides to grow there vegetables and fruits. They need a lot more sustainability!
I grew up in California and from time to time I visit. My last visit was 2 years ago and as I drove through the farming valley I constantly pointed out to my husband that there was no sign of any mulching process in any farming fields. There are housing suburbs in places where farms us to be. It was pointed out to me years ago that it took a “Special kind of stupid” to build on top of fertile farmland. In my hometown trees have been taken down in the park and I asked the person in charge “Why were none of the trees removed chipped and put down to protect the soil”? He answered “It was decided they would be burned and used for making power”.